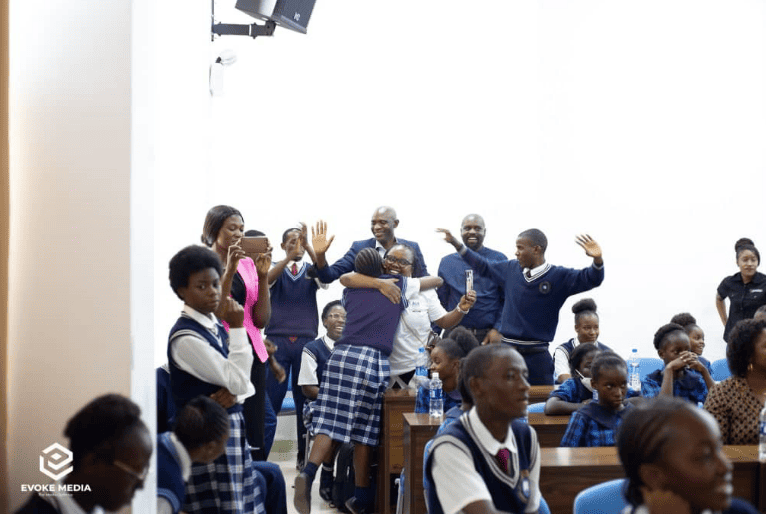
Empowering Young Learners: The Success of the Young WASH Voice Campaign and WASH Hackathon in Lusaka
Water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) are fundamental elements of sustainable development and are critical for the health and well-being of individuals and communities. However, many children, teachers, and pupils still face challenges related to inadequate WASH facilities in their schools and communities. The lack of safe water, adequate sanitation, and hygiene facilities leads to poor health, absenteeism, and a compromised learning environment.
The Centre for Water, Sanitation and Rehabilitation (WASAReC) and the Chevening Alumni Association of Zambia (CAAZ) organized a WASH hackathon competition on 24th February 2023. The participating schools are part of the Green Schools Partnership Program (GSPP), an initiative implemented under the Lusaka Water Security Initiative and supported by GIZ’s Natural Resources Stewardship (NatuReS) Programme.
The hackathon was the culmination of the Young WASH Voice Campaign (YWVC), which aimed to build capacity in school-going children aged 10 to 17 years in climate-resilient WASH governance and to provide these young learners with a platform to identify and suggest WASH solutions in their schools and communities.
Empowering Pupils to Contribute to WASH Solutions in Their Schools
The campaign recruited 120 pupils from four schools in Lusaka: Chakunkula Combined School, Foxdale Secondary School, Mumana Primary School, and New Ng’ombe Primary School. Before the start of the hackathon, the participants attended guest lectures on climate-resilient and inclusive WASH in schools and communities for four weeks. This was followed by eight weeks of mentoring learners in the problem ideation process and public speaking to support them in identifying WASH problems and their sustainable solutions. Through this process, the learners also got prepared to communicate their ideas to different audiences effectively.
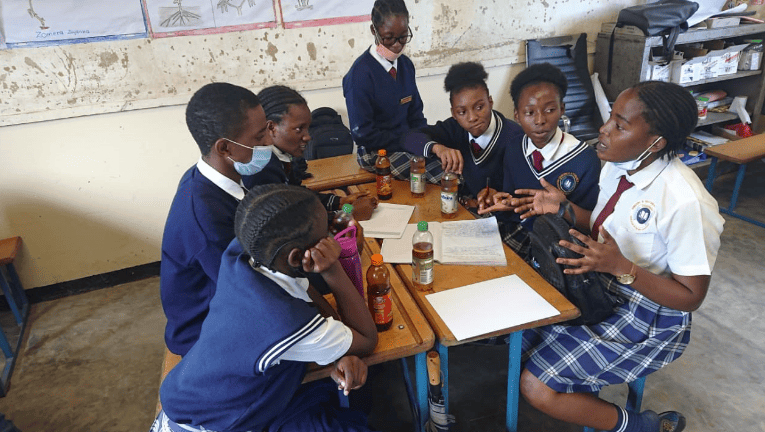

Learning and problem identification focused on four thematic areas:
- Inclusive sanitation and solid waste management
- Menstrual hygiene management, hygiene promotion, and water security
- Development of a school WASH Handbook covering these topics, games, and the WASH alphabet
- Other materials developed included the WASH Hackathon Workbook, the Hackathon Process pamphlet, and posters.
Empowering Change: The Key Results and Achievements of the WASH Hackathon
The learners and teachers were pleased with the training received and had a chance to participate in the hackathon actively. With the lectures and mentorship, the pupils were able to identify their challenges and gain knowledge on WASH stewardship. The campaign equipped 120 learners with climate-resilient and inclusive WASH knowledge to become champions of change in their schools and communities.
The outcome of the hackathon was the identification of several WASH challenges in each of the four schools. These included the lack of menstrual hygiene management facilities, water shortages in the dry season, unsafe toilets shared between older learners and pre-schoolers, vandalism of water facilities, and poor solid waste management in schools and communities.
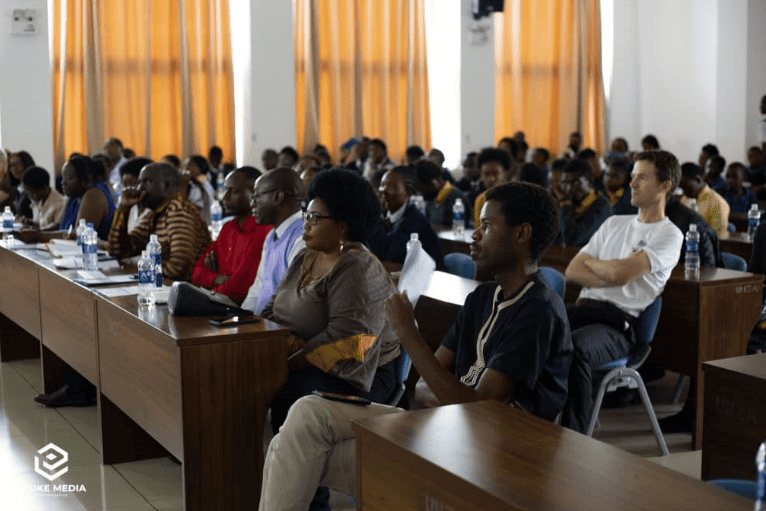

The hackathon provided an opportunity for learners to actively participate in identifying WASH challenges in their schools and communities and propose sustainable solutions. The documented priority challenges that the learners perceived can serve as a reference for WASH implementers when considering supporting schools in improving WASH service access and stewardship.
Moreover, the hackathon achieved some results in addressing the identified challenges. Some schools received support to increase water storage capacity to mitigate water shortages, especially during the dry season. Additionally, some schools received support to run water quality tests and received chlorine donations to improve access to safe drinking water.
The documented challenges can inform WASH implementers in their efforts to improve WASH service access and stewardship in schools and communities.
Summary of the Achievements:
- 120 learners equipped with climate-resilient and inclusive WASH knowledge for them to save as champions of change in their schools and communities.
- Documented priority challenges as perceived by learners (service users) that WASH implementers can reference as they consider supporting schools in improving WASH service access and stewardship.
- Some schools have already received support to increase water storage capacity to mitigate on water shortages in the school, especially during the dry season.
- Some schools have been supported to run water quality tests and received chlorine donations to improve access to safe drinking water in the school.
Feedback from Teachers and Pupils:
“The way we have been trained is good, but you should also train us in basic skills like how to fix a tap. Also, give sensitizations to all pupils on water security and how to take care of the water facilities so that there is no more vandalism.” Grade 10 pupil, Foxdale Secondary School.
“I am confident that through this campaign, our learners are prepared to be the young WASH champions in their respective schools and communities. They will be able to champion good practices and be able to speak to be heard on WASH matters.” – Lusaka District Education Board Secretary (DEBS).
Importance of Partnership: Achieving Significant Results in a Resource-Constrained Environment
As the Mayor of Lusaka, Her Honour Ms. Chilando Chitangala noted, “Such programs are very good, as they engage children in important matters while they are young. I therefore urge the schools through the District Education Board Secretary to create WASH Clubs where this knowledge gained today may continue to be built up.” The success of the WASH hackathon and YWVC can be attributed to the collaboration and engagement of various partners who supported the initiative financially and by providing the necessary human resources and logistics. This partnership demonstrated the importance of coordination and collaboration, where each partner brought their strengths to the table, to achieve significant results even in a resource-constrained environment.
Follow-up Activities: Strengthening WASH Provision in Schools and Communities
The team behind the YWVC and WASH hackathon is already planning a follow-up event where participating schools will implement their suggested solutions. This event will provide an excellent opportunity to continue building on the knowledge gained during the Young WASH Voice Campaign and to further strengthen the partnership between various organizations involved in WASH provision. The team is looking for partners to sponsor this event.
In conclusion, the WASH hackathon competition and the Young WASH Voice Campaign were highly successful in empowering young learners and building their capacity in climate-resilient WASH governance. The pupils were able to identify their WASH-related challenges and propose feasible solutions, demonstrating the importance of engaging children in important matters while they are young. The success of this initiative can be attributed to the collaboration and engagement of various partners, highlighting the importance of partnerships in achieving significant results even in a resource-constrained environment.



















