Sharing Insights on Stewardship Partnerships at the Climate Smart Agriculture Policy Dialogue in South Africa
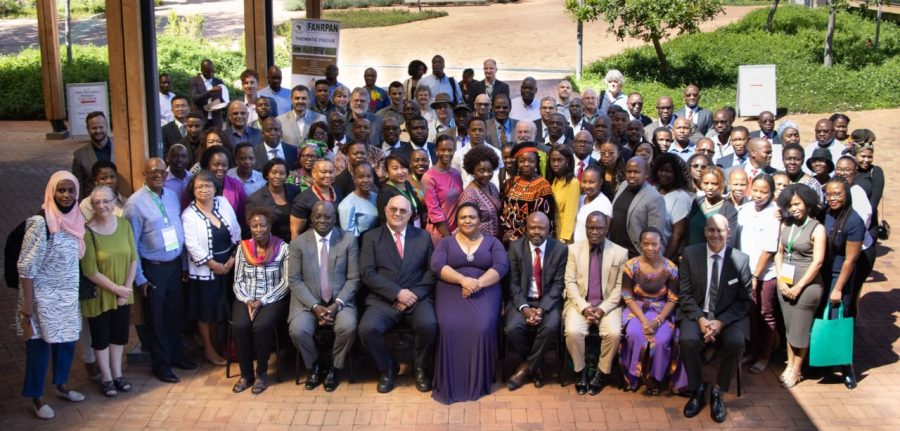

From 13-15 March 2023, stakeholders from the public sector, representatives of regional economic communities (RECs), academic and research institutions, the scientific community, and civil society gathered to share knowledge, and experience in the “Climate Smart Agriculture Policy Dialogue, transitioning to resilient farming in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA).”
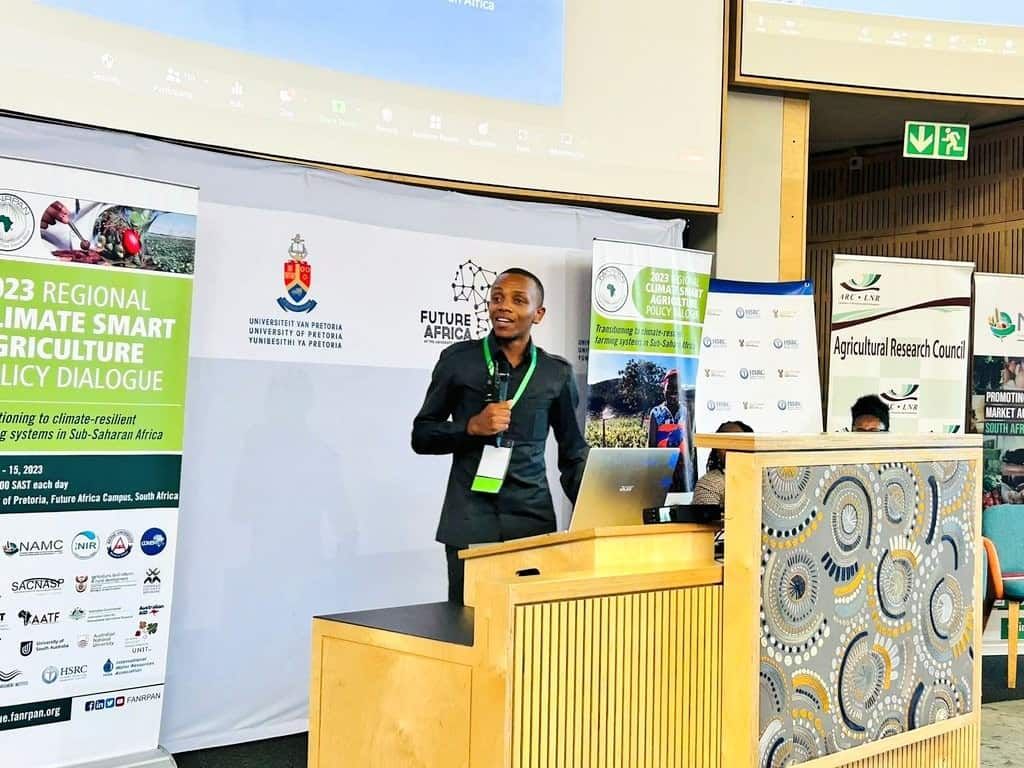
At the conference, our NatuReS colleague, Aristarick Mkenda, shared insights from stewardship partnerships in the Pangani Basin in Tanzania. The dialogue was convened by the Transforming Smallholder Irrigation in Southern Africa (TISA) consortium in collaboration with the Food, Agriculture and Natural Resources Policy Analysis Network (FANRPAN) at the University of Pretoria’s Future Africa Campus in Pretoria, South Africa. The conference theme was “Transitioning to Climate-Resilient Farming Systems in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA),” focusing on the next generation of research, smart technology, policy development and best practices.

The Climate Smart Agriculture Policy Dialogue Goals:
The Policy Dialogue aimed to accomplish the following:
- Share data demonstrating the value of climate-smart farming in SSA’s transition to resilient farming communities.
- Provide suggestions on how to scale up the development of climate-smart and resilient farming systems in SSA.
- Networking and encouraging collaborations and action
Social inclusion in the context of agriculture and food systems, water resources use, and climate action, was one of the conference’s important sub-themes. Communities, women and youths crucially contribute to agriculture and SSA catchments as farmers, workers and entrepreneurs. Depending on the regions, these groups face distinct constraints that reduce their productivity and limit their contributions to agricultural production, family livelihoods, and economic growth. As a result, the importance of context-sensitive and inclusive approaches to support them was emphasized.
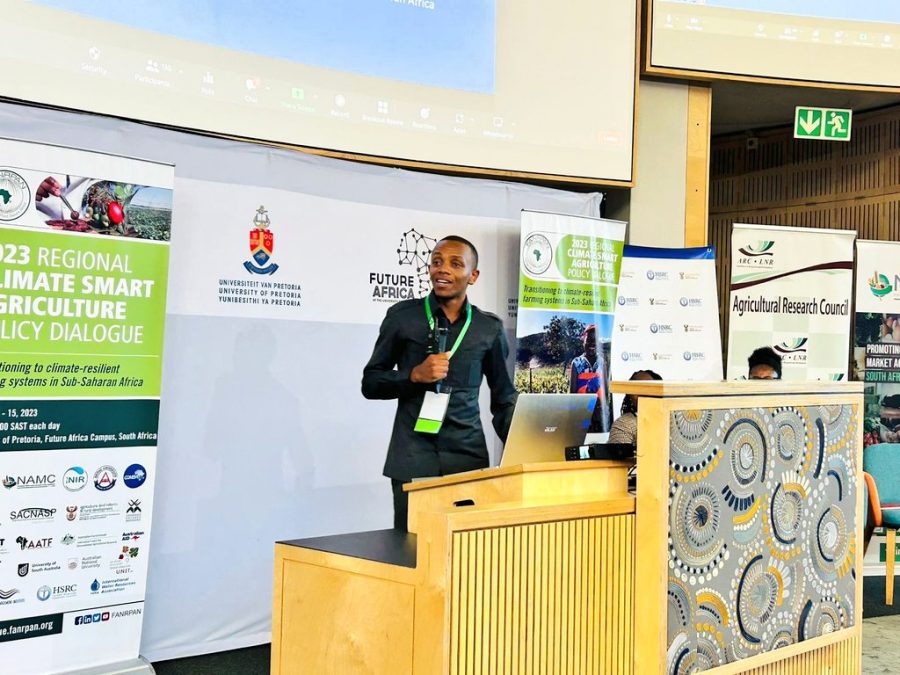

Presentation on: Addressing Water Security through Water Stewardship Partnerships. Experiences from the Pangani Basin in Tanzania
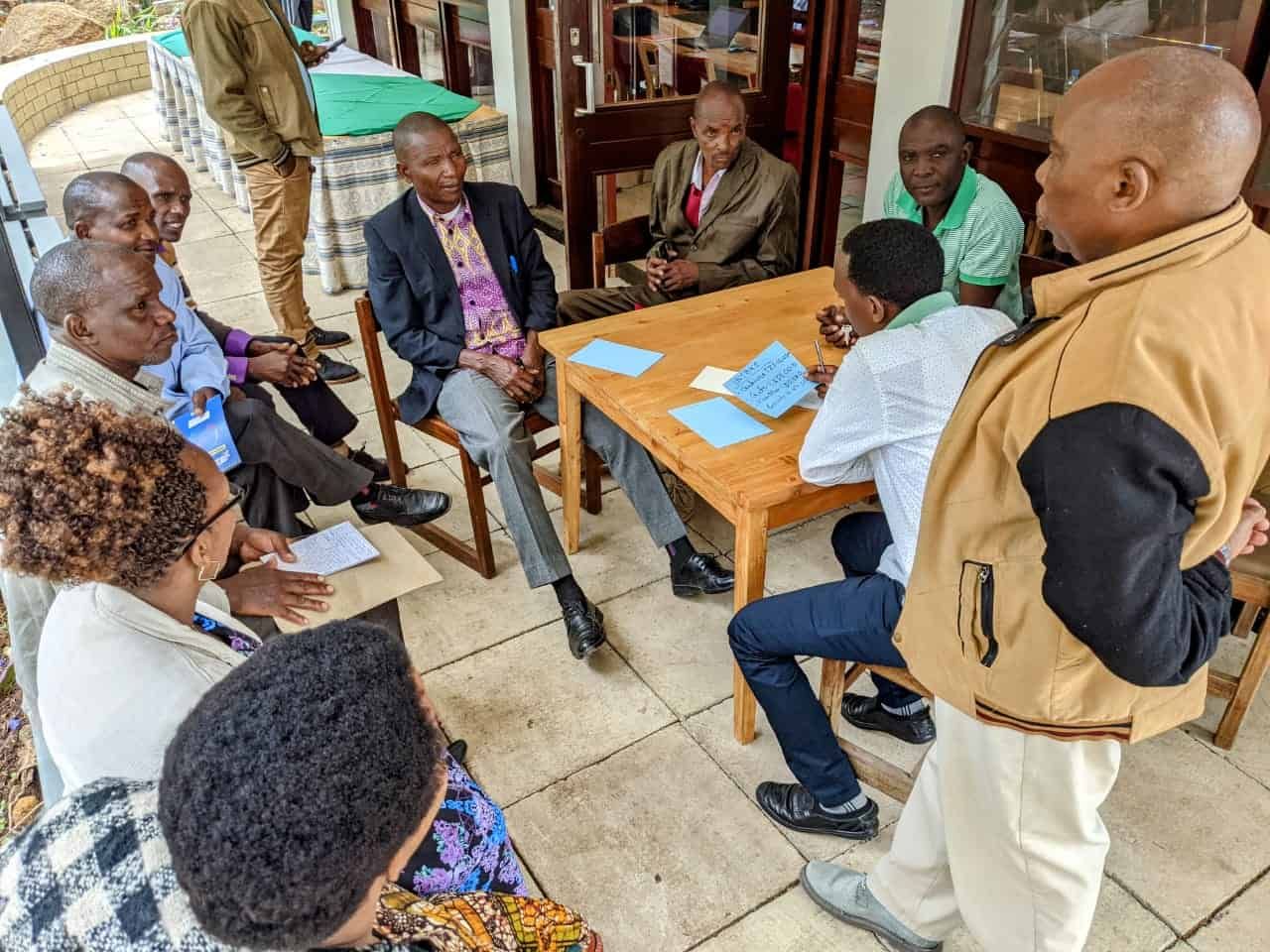
NatuReS colleague Aristarick Mkenda shared perspectives on stewardship partnerships as a possible solution to increase effective stakeholder participation and representation to address shared challenges in water-stressed catchments. Sustainable and participatory water management, thereby, is fundamental to sustainable agriculture. His presentation was based on his co-authored scientific article (Richards et al., 2022) for the Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) that analysed the partnership approach as a solution for inclusive participation. The partnerships facilitated by NatuReS in the Pangani River Basin in Tanzania served as empirical data.
Stewardship partnerships answer other IWRM implementation gaps. For example, additional financing from private sector partners can overcome the need for more funds to implement projects.
A productive discussion with the participants followed the presentation, in which challenges and their possible solutions of stewardship partnerships were discussed, such as costs of participation and balanced involvement of the private sector.
Collaboration to Address the Growing Complexity in the Agricultural Sector
In the concluding remarks of the conferences, Prof. Jammie Pittock from Australian National University (ANU) highlighted that the objectives in the agricultural sector have become much more complicated since they have grown from simply producing food to cover diverse societal needs and adapting to climate variability. The complexity of the issues and topics in agriculture is making collaborations and partnerships between individuals and sectors more important now than ever.
We thank the “Climate Smart Agriculture Policy Dialogue” and its inspiring participants for the invitation and the productive conference days and are looking forward to more valuable exchanges.
For more information about addressing water security through water stewardship partnerships, you can access the research article here.